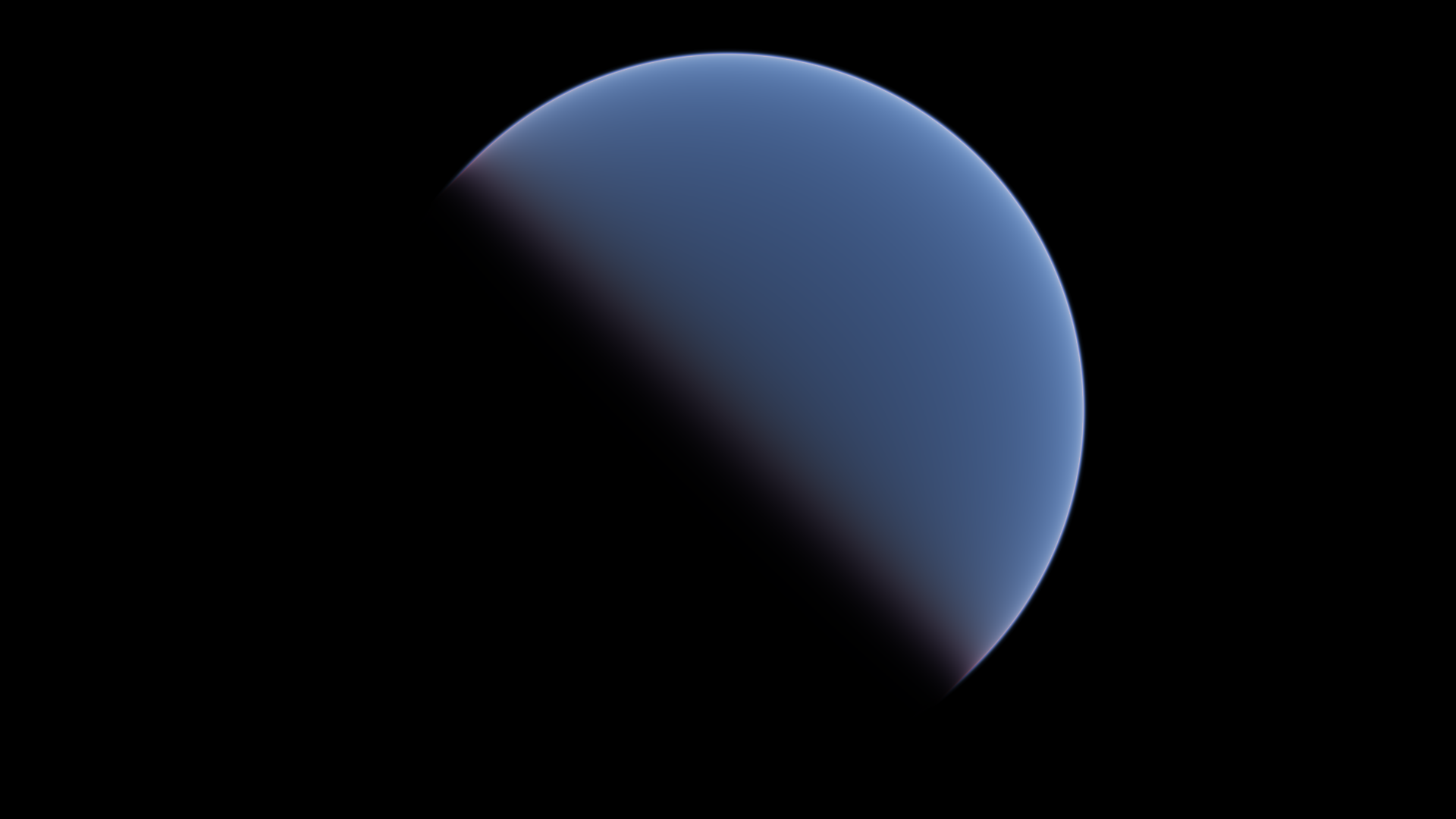
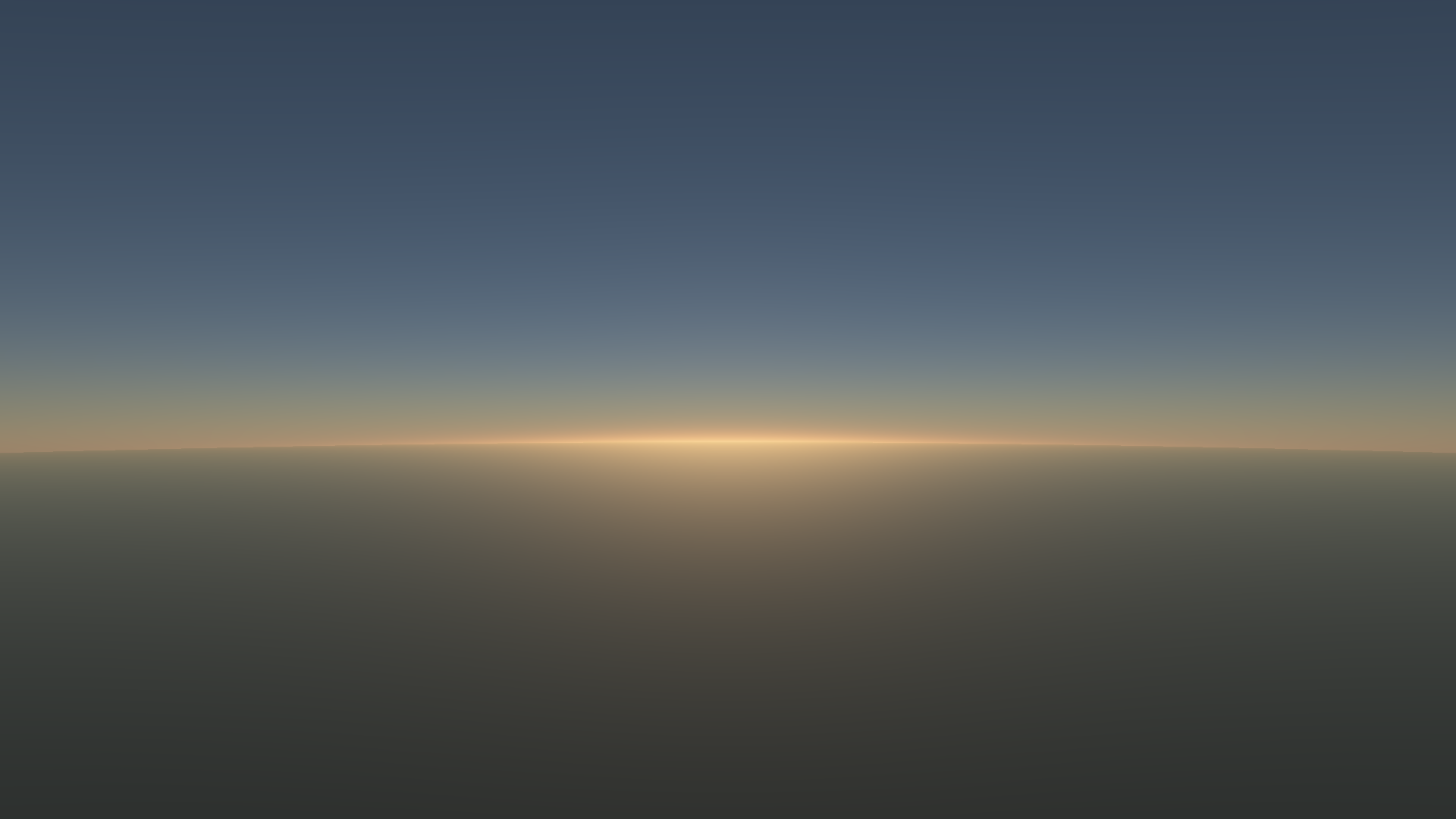
A visual and performance comparison of atmospheric scattering models
Masters thesis done at Utrecht University.
Abstract
Previous models of atmospheric scattering have either utilized an analytical fitted function, limiting the viewer to the ground, or a number of lookup tables improve runtime performance. This work introduces 3 new models, one neural network based model that supports both ground and space views, one analytical model that does not require fitting on reference data, and one model using an approximation of the transmittance tables. The new models are compared to the existing models, as well as a path traced reference, on visual accuracy, runtime performance, and implementation complexity.
Links:
Shaders, as implemented on Shadertoy:
Pretty images: